Protein
No other ingredient is as highly prized as protein. By supplementing with protein your body will recover from exercise more quickly and be provided with the raw material to build up your muscle mass, improve performance and enhance body composition, because you exercise your protein needs are higher than a sedentary person.
Read more
Showing 16/247 results
(93)
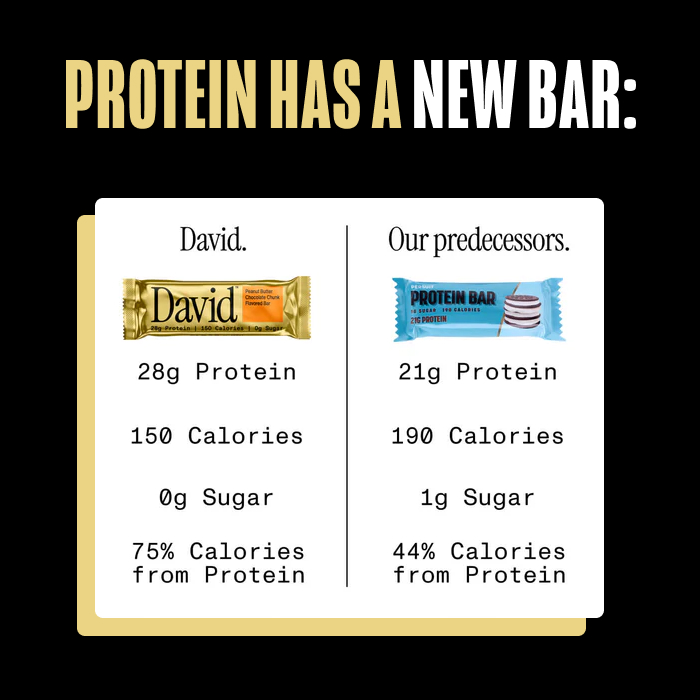
David
David Protein Bar
From£3.99
(95)
Per4m
Per4m Whey Protein
From£28.99£26.87
(135)
Scitec Nutrition
100% Whey Protein Professional
From£15.98£14.38
(41)
PEScience
Select Protein
From£14.99£14.32
(263)
Predator Nutrition
Predator Whey
From£44.98£35.98(57)
Dymatize
ISO 100
From£43.99
(34)
Mutant
Mutant Mass
From£24.98£23.92
(213)
Optimum Nutrition
Gold Standard 100% Whey
From£33.98£32.45(49)
RX Bar
RX Bar
From£31.99(43)
Musclemeds
Carnivor
From£31.98(170)
Quest Nutrition
Quest Bars
From£28.99
(15)
BioTechUSA
Iso Whey Zero
From£17.99£17.36
(52)
Optimum Nutrition
Serious Mass
From£34.99£33.50(56)
USN
Muscle Fuel Anabolic
From£63.98(21)
Dymatize
Elite Whey
From£30.98(48)